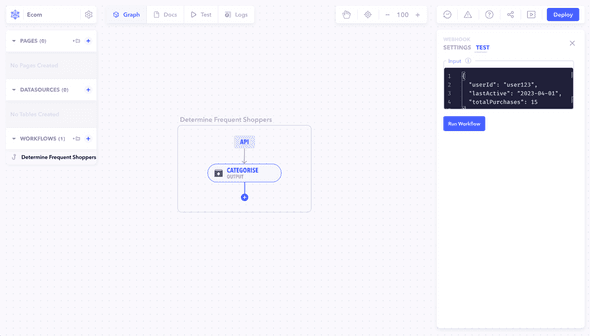
In a Canonic workflow, thoroughly testing each node ensures they function correctly and handle data as expected. This involves simulating real-world scenarios and inputs to validate each node's behavior.
Understanding Node Testing
Testing a node involves setting up conditions and inputs that the node will process. This is critical for workflows dealing with complex logic or data transformations.
Preparation
- Select the Node for Testing: Identify the node in your workflow you want to test.
- Understand the Node's Role: Know what the node is supposed to do—whether it's data processing, decision-making, or triggering other actions.
Test Data Creation
- Identify Input Requirements: Determine what kind of data the node expects. This might be strings, numbers, JSON objects, etc.
- Create Representative Data: If the webhook required an input data craft test data that accurately represents the different types of inputs the node might handle in a real-world scenario.
Example Scenario: User Data Processing
Imagine testing a node designed to categorize users based on their activity.
Test Data
{
"userId": "user123",
"lastActive": "2023-04-01",
"totalPurchases": 15
}Testing individual nodes within Canonic workflows is essential for ensuring accuracy and efficiency. This guide outlines the expected behavior, node function, testing process, and best practices.
Expected Behavior
- Frequent Shopper: If
totalPurchases> 10. - Active User: If
lastActiveis within the last month.
Node Function
Your node might contain logic to categorize users based on these criteria.
Running the Test
- Inject Test Data: Manually input the test data into the node.
- Execute Node: Run the node within the workflow.
- Observe Output: Check the node’s output or subsequent actions triggered by it.
Analyzing Results
- Match Expectations: Ensure the node's output aligns with the expected categorization.
- Error Checking: Look for any errors or unexpected behavior in the node's operation.
Comprehensive Testing Strategy
- Multiple Scenarios: Test the node with various data scenarios, including edge cases.
- Error Paths: Include test cases where errors are expected to ensure the node handles them gracefully.
Best Practices
- Consistent Review: Regularly revisit and test nodes, particularly after modifying the workflow.
- Detailed Documentation: Keep a record of test cases and results for future reference.
- Collaborative Testing: Involve team members in testing to get diverse perspectives on the node’s functionality.
Note: Thorough testing of individual nodes is a key aspect of building reliable and efficient workflows in Canonic. It’s not just about checking if a node works; it’s about ensuring it works correctly under all expected conditions.