Overview
Components in a system can be categorized as either static or dynamic. Static components have their values set at design time and cannot be changed during runtime. On the other hand, dynamic components have values set at runtime, allowing for flexibility and adaptability.
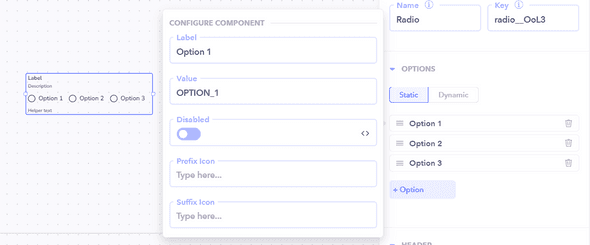
Static Components
Static components are configured at design time, and their values remain constant throughout runtime. Examples include manually setting field values and configuring static parameters.
Dynamic Components
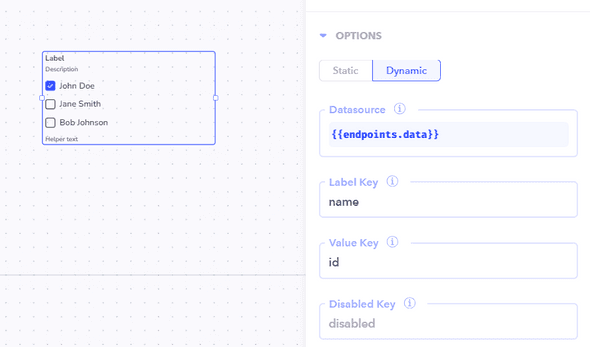
Dynamic components, in contrast, have values set during runtime. This allows for the flexibility to adapt to changing conditions or input data. For instance, values for fields can be obtained from a selected table row or a workflow output.
To implement dynamic components, pass the dataset into the data source. In the label key and value key fields, specify the corresponding keys from the dataset. For example, if the dataset looks like this:
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe",
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Jane Smith",
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Bob Johnson",
}
]Specify the label key as "name" and the value key as "id." This ensures that the "name" is displayed in the label, while the "id" is displayed in the value field