Introduction
Environment variables in Canonic provide a secure way to store and manage key-value pairs, useful for configuration settings and sensitive data like API keys or database credentials.
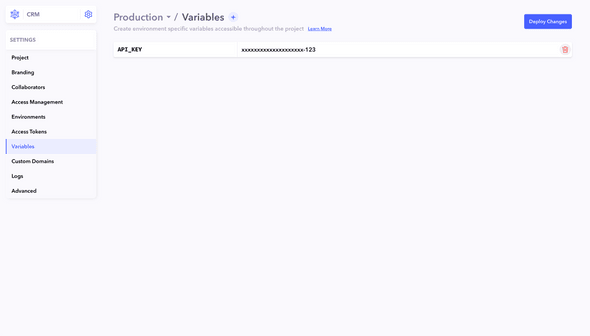
Setting Up Environment Variables
- Project Settings: Go to the settings of your Canonic project.
- Environment Variables: Find the section dedicated to environment variables named Variables.
- Define Variables: Enter your key-value pairs as environment variables.
Accessing Environment Variables
In Code Editor
Within the code editor, environment variables can be accessed using params.env.
module.exports = async function (params, context) {
const fetch = require("node-fetch")
// Example of accessing an environment variable in the Code Editor
const apiKey = params.env.API_KEY
return fetch(`https://api.example.com/data?api_key=${apiKey}`)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => data)
.catch(error => {
console.error("Error:", error)
})
}In Other Workflow Components
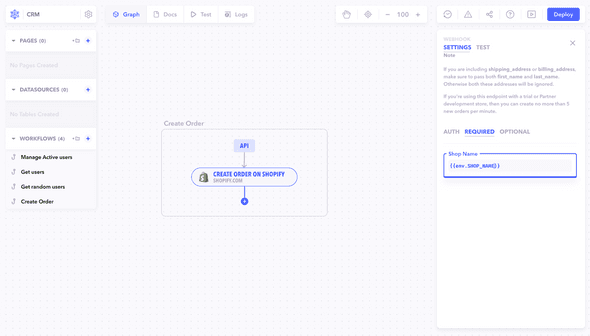
Outside of the code editor, environment variables can be accessed directly using env.
env.YOUR_ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLEBest Practices
When working with environment variables in Canonic, consider the following best practices:
- Secure Storage: Utilize environment variables for storing sensitive data, such as API keys or database credentials. This ensures the security of these critical pieces of information.
- Consistent Naming: Maintain consistency in naming your environment variables across different stages of development. This includes environments like development, staging, and production, facilitating easier management and less confusion.
Note: The effective use of environment variables is key to maintaining the security and scalability of workflows in Canonic. They play a crucial role in managing sensitive data and configuration settings in a secure and efficient manner.